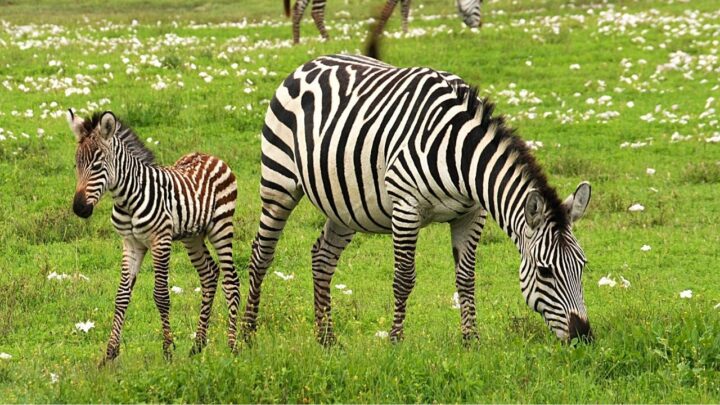
To start, it is not a myth that Zebras attack newborns that are born into their herd. Although many individuals do feel that Zebras are cute and non-vicious, this is not true.
They are attractive, but are wild animals nonetheless, and although equines they are far removed from horses and ponies in their behaviors.
Horses and ponies are domesticated and although share the same classification of mammal — equine — are as different from Zebras as wolves are from domesticated dogs.
Why Do Zebras Attack Newborns?
Zebras attack those newborns that pose a threat to the leaders of the Zebra herd. Every day in the wild, it is a “survival of the fittest” natural element that rules all behaviors. In other words, all newborns are not attacked, only those that pose a threat to the leaders of the herds of Zebras.

Why Do Zebras Attack Newborns?
Zebras Attacking Newborns
Each herd has a dominant male, and it is only the males that attack newborns who are not of their lineage. A newborn Zebra is a foul.
A Zebra foul that is born and not the offspring of the Alpha Zebra male, will in all likelihood be drowned.
This is the general method of disposing of any competitors for the females and the herd leadership.
7 Reasons Zebras Attack and Kill Newborns
1. Maintain Herd Quality and Genetics
This is an instinctive trait that is inbred into male Zebras only. Survival depends upon the size of the herd and the physical strength of each member of the herd.
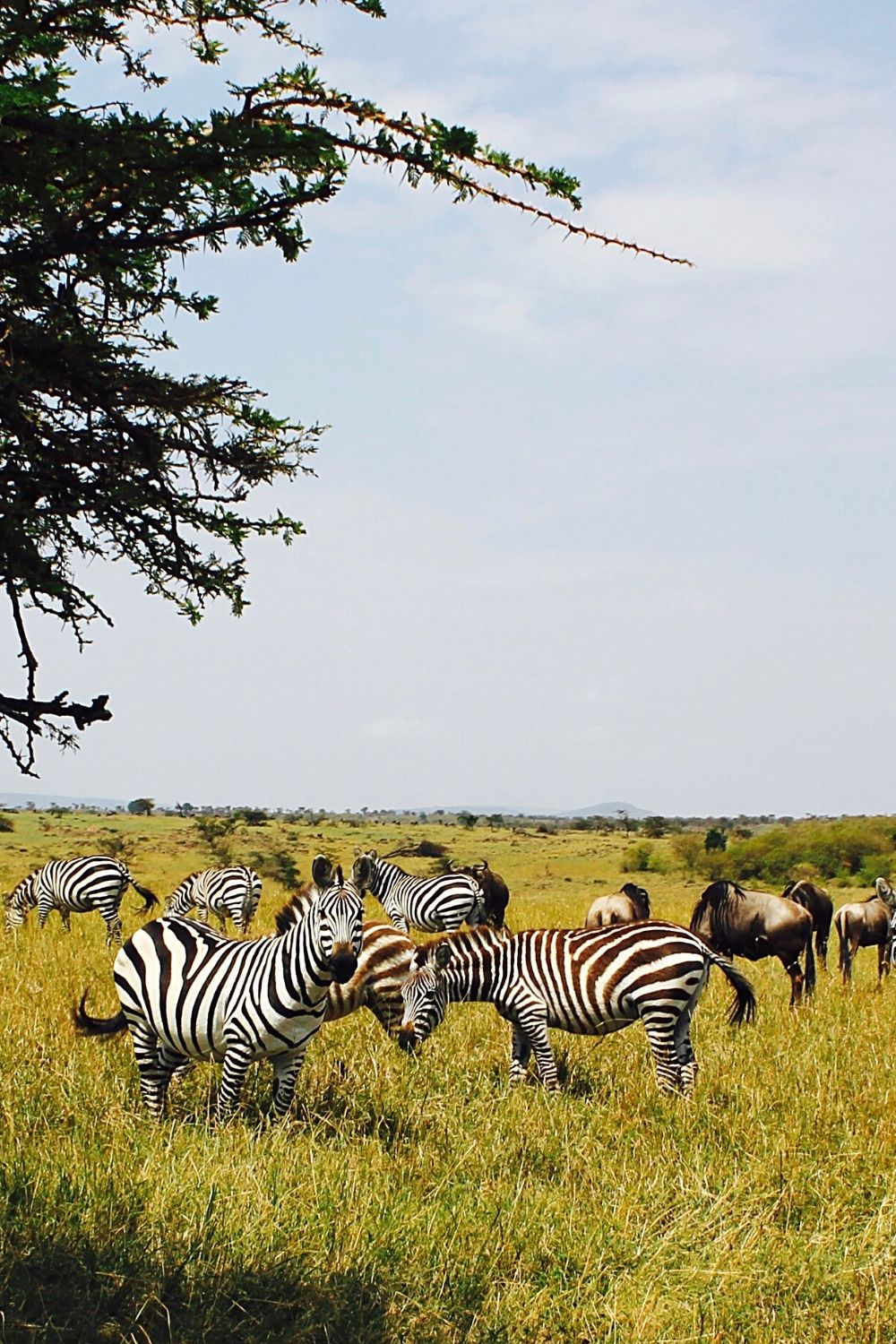

One reason why zebras attack their newborns is that they need to maintain herd quality and genetics
No male Zebra leader can afford to have weak members of the herd.
2. Preserve Male Dominance of the Herd
Male herd leaders do not welcome competition even from their own offspring. As male Zebras age and slow down they can eliminate any competition more quickly than ever.
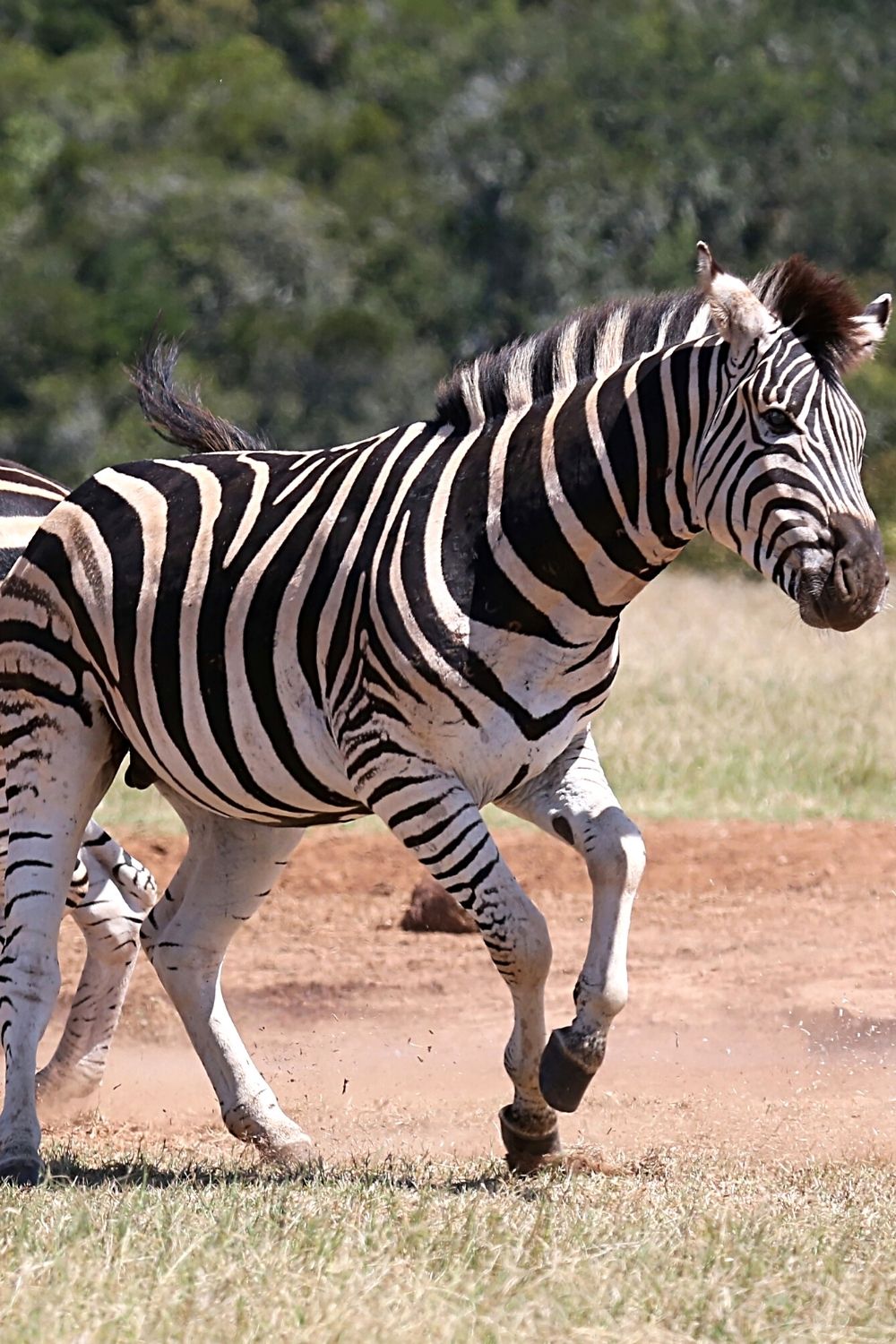

Zebras also attack their newborns to preserve their dominance (males) in the herd
Zebra Stallions do not want competition even from their own offspring.
3. Ensure that Predators are Kept at Bay
The stronger the herd in physical strength and tenacity, the better the chances of fighting off predators.

Keeping predators at bay is another reason why zebras attack their newborns
It is always a group effort to protect the entire herd and one “weak link” can leave a herd open to several losses in a few days or weeks.
4. Proving Leadership by Stallions
Once a stallion kills a foul, it is an unwritten law to the entire herd that this stallion is the herd leader and the other males are kept in line as are the females.

When zebras attack newborns, they prove their leadership to the stallions
Zebras are not kind or calm animals by nature although by their appearance most individuals do not assume this.
5. Food Preservation by Killing Newborns
In times of drought, since Zebras are herbivorous, there might be a shortage of plants and food for grazing.
Although a large herd is usually sought, too many fouls mean more “mouths to feed” and culling of the herd might occur.
Older, weaker Zebras may also be killed during a time such as this.
6. Zebras Establish a Hierarchy within Each Herd
This is witnessed by scientists and game preserves and food is imperative as Zebras eat for 80 percent of the day since the food is not nutrient-dense, only being that of plants, leaves, and grass.
7. Sexual Inclinations by Stallions
Stallions, like all male animals, are driven by testosterone and if all females in a herd are not in estrus and available for sexual activity, a foul or two might simply be killed to unleash a female’s willingness to engage in copulation.
Control of a Zebra Herd is Imperative to Males
Male Zebras are not monogamous but instead polygamous. They actually rule a harem of females within the herd.
If a female becomes impregnated by another male Zebra inside the herd, the offspring is shortly killed even if a foul is female. No other genetic lineage is acceptable to an Alpha Zebra who is also a stallion.
Stallions are non-neutered males in the equine world and are driven by testosterone.
Zebra fouls can stand minutes after birth and once the foul stands and is noticed by the Alpha male, is doomed to die if the Alpha male is not the sire.
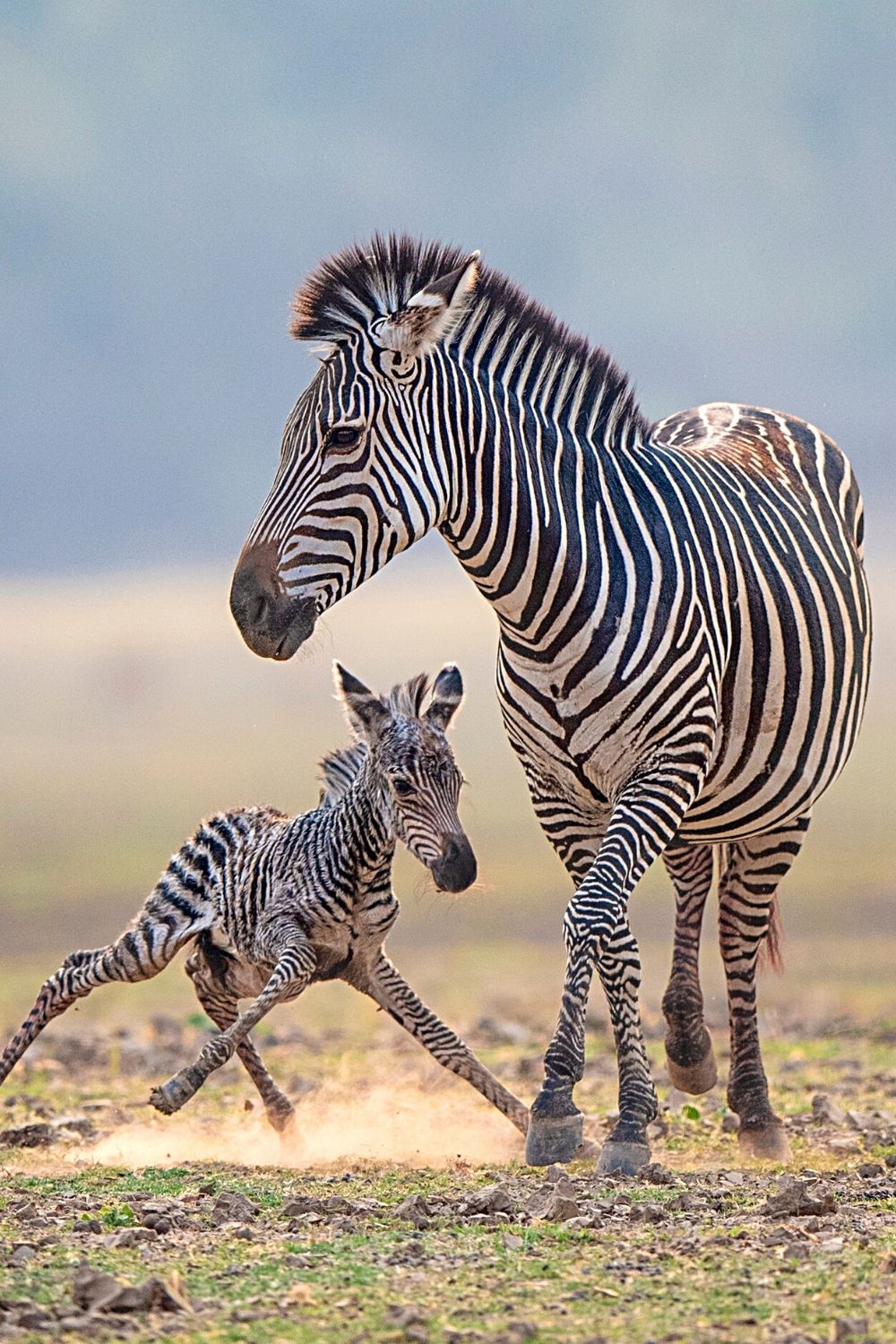

If the Alpha male isn’t the father of the zebra foul, it will kill the newborn as soon as he notices it stand
The definition of “sire” is the father of the foul.
All Zebras Exhibit Killing of Newborns
No two Zebras are alike even if they originate in the same area. Each Zebra has different stripes completely from all others.
There are mountain Zebras and African Zebras but all share the same behaviors and look completely different.
There can be Zebra varieties with long ears, some with brownish tinges, and different body lengths, but all exhibit wild behaviors that ensure herd growth for survival.
The difference in stripes confuses predators who cannot differentiate one Zebra from another when inside a herd. A swirling effect from the stripes causes predators to move on.
The larger a herd, the more the chances of surviving predatorial attacks.
Zebras are plant-eating prey for many predators and having the largest and strongest herd is the instinct driving the killing of newborn fouls by Alpha Zebras.
Zebras Have Evolved to be Fighters
When attacked by predators, Zebras fight back with their hooves which are like rocks, and their sturdy hindquarters. They also bite viciously.
Strong hooves, hindquarters, and jaws are considered the best qualities in offspring.
Genetic strength is imperative to male herd leaders. Herd leaders are the biggest and strongest Zebras so want to encourage the passing along of their genes only.
Male Zebras will also attack other males in the herd who pose a threat and Zebras battle until death with their hooves and by biting and kicking male competitors.
Only one Zebra can be the herd leader and any challenge is taken seriously.
Zebra Stallions Kill Their Own Newborns
This is hard for some individuals to believe, but to grow a herd to a large size, with the strongest Zebras in prominence, male herd leaders sometimes will kill their own sired fouls.
This is to bring a female back to estrus so that the female is ready to mate again immediately.
Estrus, also termed Oestrus is the state of female excitement in all mammals and occurs generally when non-pregnant or when not nursing.
Once a foul is killed a male herd leader might want to immediately kill it to mate again with the mother Zebra.
Frequently Asked Questions about Why Zebras Attack their Newborns
Do all Zebras engage in killing newborns?
Zebras kill their newborns but they only the male ones. Zookeepers and those who work on game preserves do separate the fouls and their mothers from all males as any male can be a threat as they view it as a chance to copulate or establish their own herd.
Can Zebras overcome killing newborns?
The males are born with the instinct to preserve their genes at all costs. The human qualities of remorse or guilt do not generally exist in wild animals.
Do female Zebras intervene in the killing of their newborns?
Female zebras do not usually intervene although there might be exceptions. However, the stallion herd leader is the decision-maker and any interference by a female might lead to her death also. Females will fight other animals for the welfare of their offspring but not the stallion.
Are Zebras stallions gentle at other times?
Even when visiting a zoo or game preserve, visitors will never be allowed to pet or feed a Zebra, even a female, as they are not mild-mannered creatures. They do have a high sense of self-preservation and will lash out at any intruders by biting and kicking.
Afterword: Why Zebras Attack Newborns
Simply put, the “herd mentality” of Zebras makes this a common practice. Self-preservation of the herd is the chief factor for the killing of newborns by Zebra stallions.
Of course, there are other factors such as food shortage and the need to copulate in males that do come into play.
Overall though, Zebras are wild animals that are born to live in the wild and the genetics they carry do drive the acts in which they engage as a herd.
Some of these same characteristics can be seen in wild horse herds across the world.
Living in the wild and inheriting wild animal gene pools play a part in all animals’ behaviors. Infanticide is appalling to humans but not to most animals.