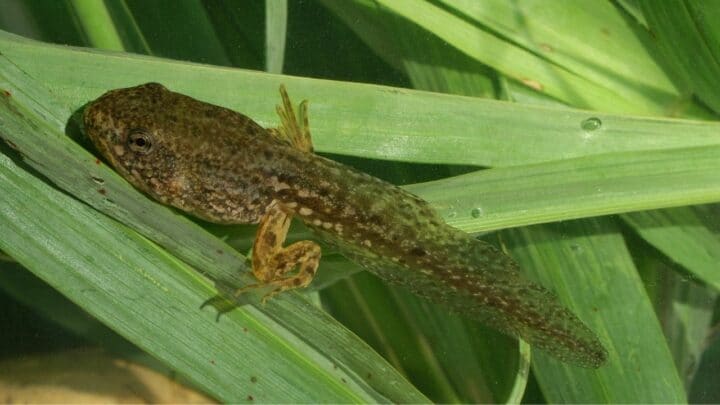
After a frog lays eggs, it undergoes a metamorphosis stage where they slowly develop from tiny tadpoles into adult frogs.
Then the tadpole finally becomes a frog.
How Long It Takes for Tadpoles to Turn into Frogs?
14 weeks are all tadpoles need to turn into frogs. During the 14 weeks, the tadpole develops both the front and back legs. The tail shrinks and nearly disappears, their gills are replaced by lungs. The frog is now ready to breed and create new tadpoles to repeat this amazing cycle of life.
Breeding and Eggs
Although not a stage in the frog’s life cycle, it is nevertheless significant. The female lays her fertilized eggs in quiet water just before breeding.
When the female frog releases the eggs, the male frogs fertilize them. There are a lot of eggs! Furthermore, they congregate to produce spawn.
The parents, in most circumstances, then abandon their eggs. Some frogs, though, continue to watch over the eggs.
The cells in the eggs divide within a couple of weeks, ultimately leading to a tadpole. The tadpoles are now ready to emerge after about three weeks.
Weekly Growth
Weeks 1 and 2: Frogspawn
Eggs are laid, they will hatch in two to three weeks.
Week 3: Hatchling Tadpoles
The first week after the tadpole hatches it is usually not visible to the naked eye.
It is tiny and does not have enough energy to swim yet. So, it blends in with the environment.
Week 4: Swimming Tadpole
About a week after the tadpole hatches it will have gained enough strength to swim and it will begin looking for food sources.
Week 6: Toothed Tadpole
Around four to five weeks of age, the tadpoles start to grow teeth and a more intricate digestive system starts to develop.
This allows their diet to expand, aiding them to eat more nutritious foods.
Week 7: Developing Tadpole
Around week five, the tadpole also starts to develop hind legs. This is a busy week for the tadpole with lots of changes.
Weeks 9-12: Froglet or Baby Frog
The tadpole completes its development and now has all its limbs, and only a very tiny tail is left, which will disappear completely within a week.
The froglet no longer has gills, it has fully developed lungs. Therefore, it can now live in both water and on land.
Weeks 13 -14: Adult Frog
That tiny little dot (tadpole) that emerged from an egg is now an adult frog. The limbs are perfectly capable of use, the lungs and the tail are gone.
The frog is now living on land and in the water and is ready to breed. This amazing transformation took place in only 14 weeks!
Tadpole Stage
They have a developed head, a long tail, and gills for breathing, and they are very little.
They had the benefit of acquiring their nourishment from the eggs up until now.
What Hatchling and Swimming Tadpoles Eat
At first, they will feed on the remains of their eggs and the jelly substance that has all the nutrients that helped them develop into tadpoles.
Up until their sixth week, they are – herbivores (eat only plant matter and vegetation). Then, I started to give my tadpoles a variety of the following foods, never overfeeding them.
Cucumber skins, duckweed, zucchini, algae, watercress, naturally decaying vegetation, kale, baby carrots, leeks, lettuce, green peppers, spinach, cabbage, detritus, green peas, moss, and mineral particles are some o of the food tadpoles eat.
Tadpoles at this stage of their life are not able to digest fruits and other foods with high protein counts, such as insects.
A tadpole’s food should be broken down before it is fed to them because their digestion is very weak.
I found that boiling or freezing minced pieces of the food listed above (not all at once but a mixture of a few is fine), feeding them about a quarter teaspoon per tadpole over a half an hour period worked very well.
You need to observe the tadpoles when they are eating to make sure all of them are getting enough food.
I had a “shy one” that hung back at mealtime and, luckily, I realized what was going on and removed that tadpole to a separate enclosure to make sure they were getting fed also and then returned it to the main enclosure after mealtime.
One last note about feeding the young tadpoles. If they do not eat all the food, be sure to remove it.
Give them an additional hour to nibble at it, then remove it because it can cause mold and bad food will make the tadpoles sick and could kill them. Only feed them once a day!
What Toothed and Developing Tadpoles Eat
Once the tadpoles develop teeth, they become carnivorous. However, they still eat vegetables and can now eat and properly digest fruits and other foods.
You can feed them all the vegetables above and any fruit, fish flakes, dead or alive aphids, tiny fish, and small bugs such as ants.
The same rule applies to feeding them small amounts over a half period and removing the leftover food after an hour.
What Adult Frogs Eat
The diet of an adult frog is mainly live insects, bugs, and even small frozen mice. They no longer need the nutrients from vegetables and fruits.
However, some frogs do enjoy them occasionally as a “treat”. I had a frog that loved strawberries! I would give it half a strawberry once a week.
Frequently Asked Questions about How Long It Takes for Tadpoles to Turn into Frogs
Do all tadpoles turn into frogs?
According to the research of 730 species of frogs, just over half of tadpoles develop into frogs. That starts with the laying of eggs in the water, hatching into tadpoles, then metamorphosing into adult frogs.
Do tadpoles die easily?
Tadpoles can die before they mature into adult frogs. For several reasons, injuries, contaminated food or water, natural cases, and other factors can contribute to tadpole death. It’s easier to see if a tadpole is alive or dead by their size if they do not grow or are the same size as other viable tadpoles, which is a strong indicator the tadpole has died.
Conclusion
The development of tadpole to adult frog is an amazing journey to watch and take part in.
Frogs make great pets and once they become adults they require very little maintenance – fresh food and water daily and a clean enclosure keeps them happy.