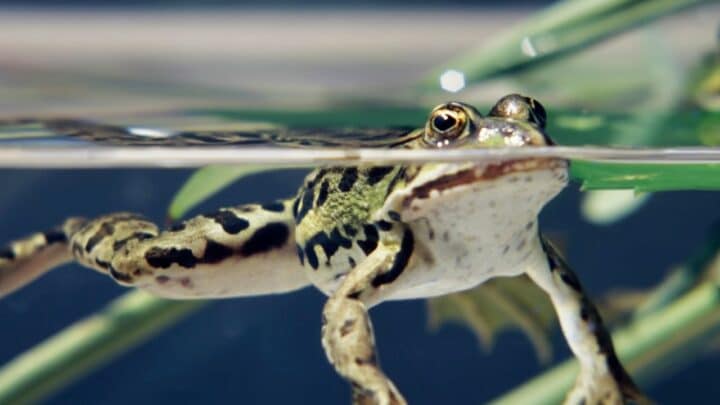
Have you ever tried holding your breath and checking how long you’ll go without resurfacing? I bet it wasn’t very long.
Would you be surprised to know that frogs are able to hold their breath for a very long time?
Let’s take a deep dive into how frogs breathe.
How Long Can Frogs Hold Their Breath?
Frogs are generally able to hold their breath between 4 and 7 hours. This is because frogs can regulate their metabolic activity, and they have the ability to breathe through their skin. There are even species of frogs that can hold their breath for months during hibernation or breathe entirely underwater.
How Long Can Frogs Hold Their Breath
Most species of frogs are able to hold their breath for 4 to 7 hours.
Let’s take a look at some unique facts about frog biology that make them so good at holding their breath.
Frogs and Underwater Breathing
Frogs are capable of breathing underwater. This is one of the various reasons why frogs are adept at breath-holding.
There are even certain species of frogs that spend their entire lives underwater. These types of frogs don’t even have the ability to breathe air like other species of frogs do.
In fact, frogs start out their life cycle as tadpoles that have gills just like fish do. They can only breathe underwater.
How Frogs Breathe
Frogs have a few different ways of breathing. Unlike mammals, which can only breathe by taking air through the lungs, frogs have a few unique tricks up their sleeves when it comes to getting oxygen in their blood.
First and foremost, frogs start out their lives with gills. Baby frogs, called tadpoles, are born with gills just like fish.
Tadpoles spend their early lives living in the water while they mature into adult frogs.
While the tadpoles are maturing, they are developing their lungs. Frogs also have lungs that are very similar to ours.
They practice a special type of breathing that is essentially swallowing large gulps of air into their lungs at once. But, lungs aren’t the only way that frogs can breathe.
Frogs practice a unique kind of breathing known as cutaneous breathing.
Cutaneous breathing enables frogs to absorb the dissolved oxygen through their skin. This is one of the reasons why frogs can stay underwater for so long without needing to surface for air.
Species of Frog That Can Hold its Breath the Longest
There are some species of frogs that spend their whole lives underwater. The African Clawed Frog and the Western Clawed Frog are just two examples of frog species that spend all of their time in the waves.
These frogs do need to surface for air occasionally, but they spend most of their time holding your breath underwater.
Frogs also hibernate through rough weather and tough seasons. Respiration slows down during hibernation periods.
This means that frogs can hold their breaths for long periods while they are hibernating through the colder months.
The Wood Frog can technically hold its breath throughout all of the winter. This frog is capable of being frozen solid and surviving when it falls out next spring.
This is because its blood is able to produce a protective antifreeze that keeps the frog safe during these cold months.
How Long Can Toads Hold Their Breath
Toads are just a different classification of frogs. The big difference between toads and frogs is that toads are adapted to spend more time on land.
However, toads are still capable of holding their breaths for long periods. Toads can hold their breath equal to that of even the most aquatic frogs.
Why Frogs Puff Out Their Throats
You might think that a frog is trying to hold its breath when it puffs out its throat, but it’s actually trying to communicate.
That inflatable throat is called the frog’s vocal sac. The frog inflates its vocal sac in order to create a louder croaking sound.
Frogs use these sounds to communicate for a variety of reasons. One of the big reasons frogs use their vocal sacs to communicate is during their mating seasons.
The next time you see a frog puffing out its throat, just know it’s trying to talk to other frogs and not trying to hold its breath.
Frequently Asked Questions about How Long Frogs Can Hold Their Breath
Do Frogs Need to Come Up for Air?
This answer gets a little complicated. There are certain frog species like the Bornean Flat-Headed that breathe only through their skin. In fact, the Bornean Flat-Headed frog doesn’t even have lungs! This means that the Bornean Flat-Headed frog never needs to come up for air. However, other species of frogs do have lungs in addition to being able to breathe through their skin. These frogs will need to surface for air if the water around them runs low on oxygen. This can happen in stagnant pools of water.
Can Frogs Drown?
Many species of frogs have lungs just like people do. If these lungs become flooded with water, the frogs can drown. Frogs are expert swimmers and are less likely to drown than animals who don’t spend much time in the water.
How Long Can a Frog Stay Out of Water?
This is an interesting question to answer. Some frogs like the Green-Striped Burrowing frog (Cyclorana alboguttata) have been observed spending up to 3 months hiding away in dry soil while it waits through droughts until the rains come. More common species of frogs can only live for a few days when deprived of water.
Wrapping Up: How Long Can Frogs Hold Their Breath
So, how long can frogs hold their breath? Most species of frogs can hold their breath between 4 to 7 hours, but there are special conditions that can cause frogs to hold their breath for months at a time.
Frogs are certainly an interesting species that have adapted multiple ways of breathing and holding their breath.